Penggunaan Gel Polimer Super Penyerap dalam Pengekstrakan Minyak Kelapa Dara melalui Fermentasi Semulajadi
Abstract
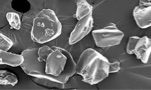
Penyelidikan ini dijalankan untuk mengkaji kesan penambahan gel polimer super penyerap (SAP) ke atas pengekstrakkan minyak kelapa dara (VCO) secara fermentasi semulajadi. Gel polimer super penyerap ini dihasilkan menggunakan kaedah penyinaran gelombang mikro dengan kehadiran natrium hidroksida (NaOH) dam kalium persulfat (KPS) sebagai pemula. Manakala N,N-metilena bisakrilamida (MBA) digunakan sebagai agen taut silang. Sampel yang terhasil telah dicirikan dan dianalisis dengan menggunakan Mikroskop Imbasan Elektron (SEM), Spektroskopi Inframerah Transformasi Fourier (FTIR) dan Analisis Termogravimetri (TGA). Analisis FTIR menunjukkan kehadiran kumpulan berfungsi amida dengan isyarat yang kuat pada puncak 1562 cm-1, 1658 cm-1 dan 3185 cm-1. TGA pula menunjukkan bahawa sampel ini mempunyai tahap kestabilan terma yang tinggi. Mikrograf SEM membuktikan terdapat liang-liang di permukaan gel polimer yang berukuran lebih kurang 1 - 2 mikron yang sangat sesuai untuk proses penyerapan. Penggunaan gel polimer ini didapati mempercepatkan pemisahan minyak dan air serta meningkatkan perolehan minyak .
Keywords
Full Text:
PDFReferences
Marina, A. M., Che Man, Y. B. & Amin, I. 2009. Virgin coconut oil: emerging functional food oil. Trends in Food Science and Technology. 20(10) :481–487. Retrieved from http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.tifs.2009.06.003
Brian, S. & Marianita, S. 2004. Virgin Coconut Oil - How It Has Changed People's Lives, and How It Can Change Yours!. USA : Sophia Media.
Nik Norulaini, N. A., Setianto, W. B., Zaidul, I. S. M., Nawi, A. H., Azizi, C. Y. M. & Omar, A. K. M. 2009. Effects of Supercritical Carbon Dioxide Extraction Parameters on Virgin Coconut Oil Yield and Medium-Chain Triglyceride Content. Food Chemistry 116(1): 193-197.
Pourjavadi, A., Soleyman, R.& Bardajee, G.R. 2009. Novel Superabsorbent Hydrogel Based on Natural Hybrid Backbone: Optimized Synthesis and its Swelling Behavior. Bulletin of the Korean Chemical Society 30:2680-2686.
Shi, X.N., Wang, W.B.& Wang, A.Q.2011. Effect of Surfactant on porosity and Swelling behaviors of guar gum-g-poly(sodium acrylate-co- styrene)/attapulgite superabsorbent hydrogels. Colloids and surfaces B: Biointerfaces 88: 279-286.
Kabiri, K., Omidian, H. & Hashemi, S. A. 2003. Synthesis of fast-swelling superabsorbent hydrogels : effect of crosslinker type and concentration on porosity and absorption rate 39 :1341–1348.
Omidian, H., Hashemi, S. A., Sammes, P. G. & Meldrum, I. 1998. A model for the swelling of superabsorbent 39(26) :6697–6704.
Yin, L., Fei, L., Cui, F., Tang, C.& Yin, C. 2007. Superporous Hydrogels Containing Poly(acrylic acid-co-acrylamide)/O-carboxymethyl Chitosan Interpenetrating Polymer Network. Biomaterials 28: 1258-1266.
Pourjavadi, A., Soleyman, R.,Ghasemzadeh, H.& Salimi, H. 2010. CMC/Celite Superabsorbent Composites: Effect of Reaction Variables on Saline- absorbency under Load. Iranian Polymer Journal 19: 571-579.
Pandey, M., Amin, M.C., Ahmad, N.& Abeer, M.M. 2013. Rapid Synthesis of Superabsorbent Smart- Swelling Bacterial Cellulose/Acrylamide-Based Hydrogels for Drug Delivery. International Journal of Polymer Science, Article ID 905471: 1-10.
Kalaleh, H., Tally, M. & Atassi, Y. 2013. Preparation of a Clay Based Superabsorbent Polymer Composite of Copolymer Poly (acrylate-co-acrylamide) with Bentonite via Microwave Radiation. Research& Reviews in polymers 4: 145- 150.
Pourjavadi, A.& Hosseinzadeh, H. 2010. Synthesis and Properties of Partially Hydrolyzed Acrylonitrile-co -Acrylamide Superabsorbent Hydrogel. Bulletin of the Korean Chemical Society 31: 3163-3172.
Refbacks
- There are currently no refbacks.
Call for Submissions
We welcome submissions for the coming issue that will be officially published in March 2022. We are committed to providing results of reviewing within two weeks, and publishing the paper within one month from the submission date (subjected to responses by authors). This means accepted papers will be available online even before the issue is published officially.
Publons Partners
Journal of Polymer Science and Technology (JPST) is now one of Publons Partners. This means biodata of reviewers in Publons will be automatically updated once reviewing on articles submitted to JPST is completed (subjected to terms and conditions).
How to promote journal articles
Promoting your journal article is imperative to maximise the exposure, enhance the discoverability and increase engagement with readers and other academics. Together with the publisher, as an author, you can help to promote your newly published articles via the following:
1) Institutional webpage.
Provide the link of your latest article in your institutional website. The webpage visitors who view your profile will be able to see your latest research and publications.
2) Social media.
The rise of the social media has also profoundly affected the publishing fraternity. More and more users have chosen the social media platforms as a way of sharing. Social media sharing helps foster convenient dissemination of information, which can be achieved within a short time. You can share your article in major online social media platforms including Twitter, Facebook, LinkedIn and so on.
3) Utilise scholarly networking and reference platforms.
A scholarly or academic networking platforms such as Academia.edu, MyNetResearch, ResearchGate, Mendeley and so on are indeed useful as they help bring scholars of common areas of expertise close together.
4) Press Releases.
If your article involves a new, significant or important discovery, consider linking up with media organisations for a press release. This brings your work to the mainstream media.
5) Blog.
If you keep a personal blog, you can get your blog readers updated with the list of your most recently published articles and the development in your area of research. Linking your article in your personal blog can vastly enhance the discoverability. Discuss briefly about the article and how the users might benefit from it.
6) Add to reading list or assignment.
Add your article (or the journal your article is published) as essential reading to your students. You may also create related assignments, e.g. review of the article, or have them discussed about the write up in class.
7) Add to your signature.
Announce your latest publication underneath your signature. Provide a link where the article can be downloaded/viewed.