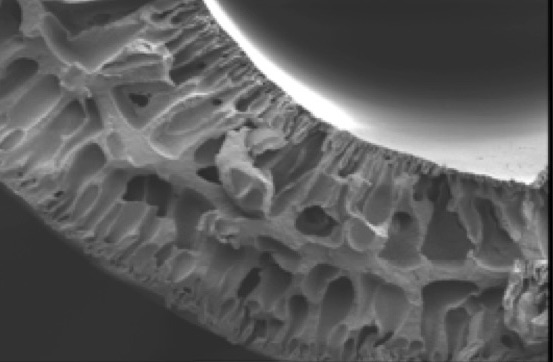
Hydrophobicity Enhancement of Poly(vinylidene fluoride-co-hexafluoropropylene) for Membrane Distillation
Abstract
A Poly (vinylidene fluoride-co-hexafluoropropylene), (PVDF-co-HFP) hollow fiber membrane was prepared by phase inversion method using different concentrations of PVP as a pore former additives in the dope solution. Surface modification was done using a formic acid through immersion technique. It was observed that the contact angle for all membranes increased due to the surfaces modification (10% of hydrophobicity increment).This study shows that the hydrophobicity of (PVDF-co-HFP) hollow fiber membrane can be enhanced via formic acid surface modification process.
Keywords
Full Text:
PDFReferences
M. Khayet, T. Matsumura. Membrane Distillation: Principles and Applications, Elsevier, Oxford, U.K. 2011.
A. Alkhudhiri, N. Darwish, N. Hilal, Membrane distillation: a comprehensive review, Desalination, 287 (2012), 2–18.
L. Song, B Li , K.K. Sirkar, J.L. Gilron, Direct contact membrane distillation-based desalination: Novel membranes, devices, larger-scale studies, and a model. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res., 46 (2007), 2307–2323.
M. M. Teoh, S. Bonyadi, T.Shung Chung, Investigation of different hollow fiber module designs for flux enhancement in the membrane distillation process Journal of Membrane Science., 311 (2008), 371–379.
A.L. Ahmad, A.A. Abdulkarim, B.S. Ooi, S. Ismail, Recent development in additives modifications of polyethersulfone membrane for flux enhancement, Chemical Engineering Journal, 223 (2013), 246-267.
Z. Jianhua, J. D. Li, M. Duke, Z. Xie, and S. Gray. "Performance of asymmetric hollow fibre membranes in membrane distillation under various configurations and vacuum enhancement." Journal of Membrane Science. 362 (2010), 517-528.
Z. Jianhua. Theoretical and experimental investigation of membrane distillation. Diss. School of Engineering & Science, Victoria University, 2011.
L. Shi, R. Wang, Y. Cao, D. T. Liang, J. H. Tay. Effect of additives on the fabrication of poly(vinylidene fluoride-co-hexafluropropylene) (PVDF-HFP) asymmetric microporous hollow fiber membranes. Journal of Membrane Science. 315 (2008), 195–204.
W.-Y. Chuang, T.-H.Young, W.-Y.Chiu, C.-Y. Lin. The effect of polymeric additives on the structure and permeability of poly(vinyl alcohol) asymmetric membranes. Polymer. 41 (2000), 5633–5641.
J. Bumsuk, J. K. Yoon, B. Kim, and H.W. Rhee. Effect of molecular weight of polymeric additives on formation, permeation properties and hypochlorite treatment of asymmetric polyacrylonitrile membranes." Journal of membrane science 243,(2004): 45-57.
Refbacks
- There are currently no refbacks.
Call for Submissions
We welcome submissions for the coming issue that will be officially published in March 2022. We are committed to providing results of reviewing within two weeks, and publishing the paper within one month from the submission date (subjected to responses by authors). This means accepted papers will be available online even before the issue is published officially.
Publons Partners
Journal of Polymer Science and Technology (JPST) is now one of Publons Partners. This means biodata of reviewers in Publons will be automatically updated once reviewing on articles submitted to JPST is completed (subjected to terms and conditions).
How to promote journal articles
Promoting your journal article is imperative to maximise the exposure, enhance the discoverability and increase engagement with readers and other academics. Together with the publisher, as an author, you can help to promote your newly published articles via the following:
1) Institutional webpage.
Provide the link of your latest article in your institutional website. The webpage visitors who view your profile will be able to see your latest research and publications.
2) Social media.
The rise of the social media has also profoundly affected the publishing fraternity. More and more users have chosen the social media platforms as a way of sharing. Social media sharing helps foster convenient dissemination of information, which can be achieved within a short time. You can share your article in major online social media platforms including Twitter, Facebook, LinkedIn and so on.
3) Utilise scholarly networking and reference platforms.
A scholarly or academic networking platforms such as Academia.edu, MyNetResearch, ResearchGate, Mendeley and so on are indeed useful as they help bring scholars of common areas of expertise close together.
4) Press Releases.
If your article involves a new, significant or important discovery, consider linking up with media organisations for a press release. This brings your work to the mainstream media.
5) Blog.
If you keep a personal blog, you can get your blog readers updated with the list of your most recently published articles and the development in your area of research. Linking your article in your personal blog can vastly enhance the discoverability. Discuss briefly about the article and how the users might benefit from it.
6) Add to reading list or assignment.
Add your article (or the journal your article is published) as essential reading to your students. You may also create related assignments, e.g. review of the article, or have them discussed about the write up in class.
7) Add to your signature.
Announce your latest publication underneath your signature. Provide a link where the article can be downloaded/viewed.