PENCIRIAN ELEKTROKIMIA MENGGUNAKAN KAEDAH PEMEGUNAN DNA YANG BERBEZA UNTUK FABRIKASI BIOSENSOR DNA PORSIN
Biosensor; MPA; sisteamina; mikrosfera akrilik; DNA porsin
Abstract
Abstrak
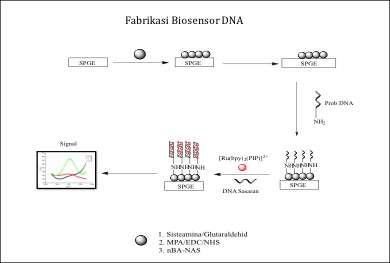
Beberapa tahun kebelakangan ini, pembangunan sensor asid deoksiribonukleik (DNA) secara elektrokimia telah berkembang dengan pesat. Salah satu langkah penting dalam fabrikasi sensor DNA elektrokimia adalah pemegunan prob DNA pada permukaan elektrod bagi memperoleh proses hibridisasi yang optimum dengan DNA sasaran. Pembinaan biosensor yang mempunyai kepekaan dan selektiviti yang baik memerlukan keberkesanan penghibridan yang tinggi dan meminimumkan penjerapan yang tidak spesifik. Oleh itu dalam kajian ini, pencirian elektrokimia menggunakan tiga kaedah pemegunan DNA berdasarkan lapisan swahimpunan sisteamina, asid 3-merkaptopropionik (MPA) dan matrik mikrosfera akrilik (nBA-NAS) telah di kaji. Antrakuinon-2-asid sulfonik monohidrat (AQMS) digunakan sebagai penanda penghibridan. Kedudukan arus puncak penurunan dan pengoksidaan penanda AQMS adalah pada keupayaan -0.72 V dan -0.66 V. Pengubahsuaian setiap lapisan menggunakan sisteamina, MPA dan nBA-NAS pada permukaan elektrod emas bercetak skrin (Au-SPEs) menunjukkan perubahan arus AQMS yang membuktikan setiap lapisan yang diubahsuai berjaya dilakukan. Hasil kajian menunjukkan hanya interaksi antara penanda penghibridan AQMS dengan DNA sasaran menggunakan MPA dan nBA-NAS memberikan rangsangan yang baik berbanding dengan sisteamina.
Kata Kunci: Biosensor; MPA; sisteamina; mikrosfera akrilik; DNA porsin
Abstract
In recent years, the interest in developing electrochemical deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) sensor has been growing. One of the essential step in the fabrication of an electrochemical DNA sensor is DNA probe immobilization on the electrode surface to achieve a good hybridization process with the target of DNA. A biosensor with great sensitivity and selectivity needs high level of hybridization efficiency and minimization of non-specific adsorption. Herein, in this study, three DNA immobilization methods based on cysteamine, 3-mercaptopropionic acid (MPA) and acrylic microsphere (nBA-NAS) were analyzed. Anthraquinone-2-sulfonic monohydrate acid (AQMS) is used as a hybridization label. The reduction and oxidation peak positions of the AQMS markers are at the potential of -0.72 V and -0.66 V. Modifications of each layer using cysteamine, MPA and nBA-NAS on the surface of screen printed gold electrode (Au-SPEs) indicate changes in the current of AQMS that proves modification of each layer was successful. The results show that only the interaction between AQMS markers with DNA target using MPA and nBA-NAS provides a good response compared to the cysteamine.
Keywords: Biosensor; MPA; cysteamine; acrylic microsphere; porcine DNA
COPYRIGHT
It is the author's responsibility to ensure that his or her submitted work does not infringe any existing copyright. Authors should obtain permission to reproduce or adapt copyrighted material and provide evidence of approval upon submitting the final version of a manuscript.